Beyond the Colosseum : A Glimpse into the Roman Empire’s Opulent Artistic Heritage
When we think of the Roman Empire, mighty gladiators and the majestic Colosseum often dominate our imagination. But there’s far more to Rome’s legacy than these iconic symbols. Many people are unaware of the vast artistic treasures integral to daily life in ancient Rome—treasures waiting to be uncovered beyond what popular culture has shown us.
Imagine a world where art wasn’t just for the elite but woven into every facet of society; this was Rome at its peak. A sculpture from 2nd-century Rome didn’t just showcase aesthetic taste—it told stories of influence, heritage, and immense cultural sophistication.
Did you know that beyond Rome’s bustling amphitheaters lie masterpieces as significant as the famed arena itself? Domus Aurea and Palazzo Massimo alle Terme stand proudly, bearing stories in stone and color waiting to be unearthed.
Our journey through this article will guide you beyond well-trodden paths, revealing an empire’s true spirit captured in art forms from sculptures to paintings. With each paragraph, navigate an ancient world where every corner brimmed with creative energy—echoes of which continue to resound today.
Key Takeaways
- Roman art includes more than just buildings like the Colosseum; it also has sculptures, paintings, and mosaics.
- The art from Rome changed over time with different styles in the Republican period, Imperial period, and Late Antiquity.
- Famous people like Praxiteles and Augustus made significant changes in Roman art.
- Everyone could enjoy Roman art because it was not just for rich people; even simple homes had decorations.
- You can learn more about Roman art online through museums or resources that show old Roman artworks and architecture.
Overview of Ancient Roman Art
Ancient Roman art, a testament to the empire’s cultural sophistication, offers us a window into an era of unparalleled creativity and grandeur. Encompassing a vast array of mediums from majestic architecture and lifelike sculpture to intricate mosaics and wall paintings, this artistic heritage reflects the diverse influences Rome absorbed from conquered territories.
The Romans didn’t solely focus on creating original styles; they were adept at adopting and adapting the aesthetics from conquered lands, ingeniously incorporating Hellenistic, Egyptian, and Etruscan motifs into their creations.
The opulence of Roman art is evident in its embrace of fine materials such as marble quarried in Carrara—used to erect timeless monuments like the Pantheon—and in detailed sculptures that mirrored societal importance, whether through heroic portraiture or depictions of deities such as Venus.
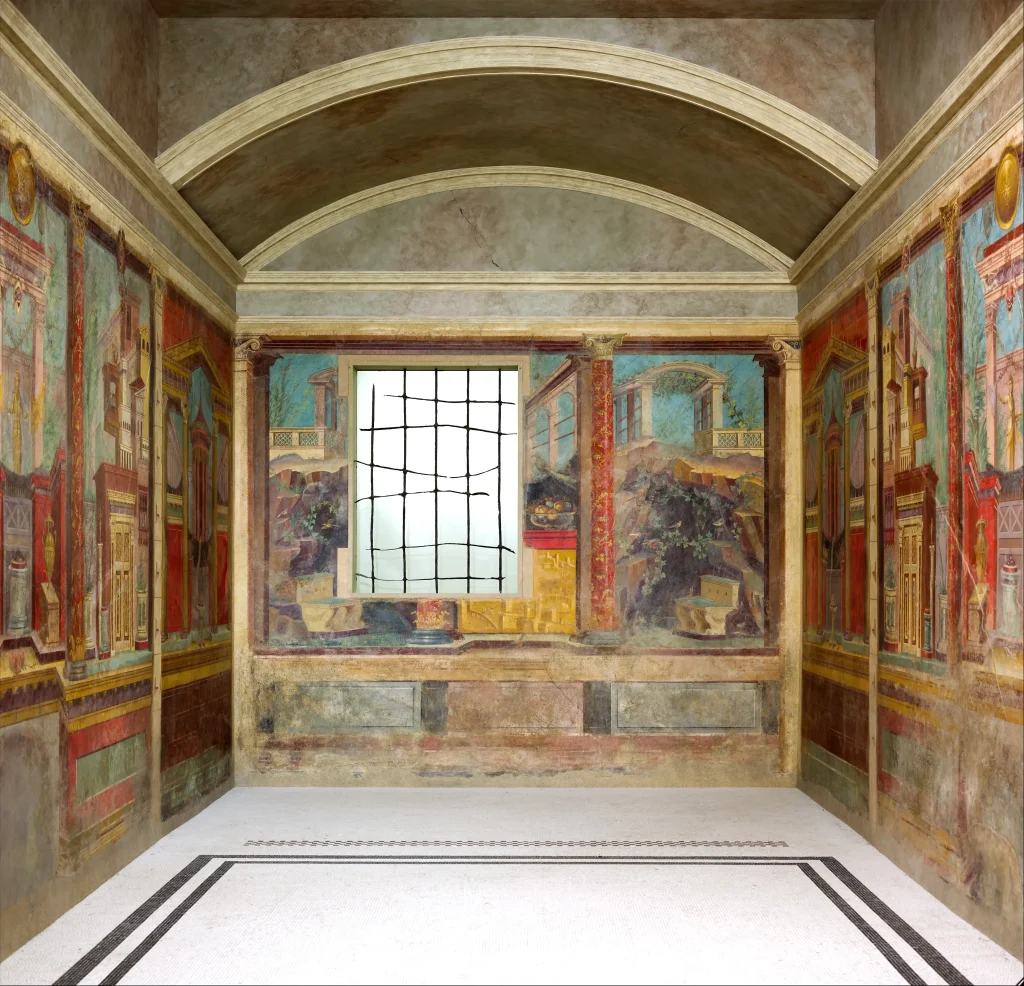
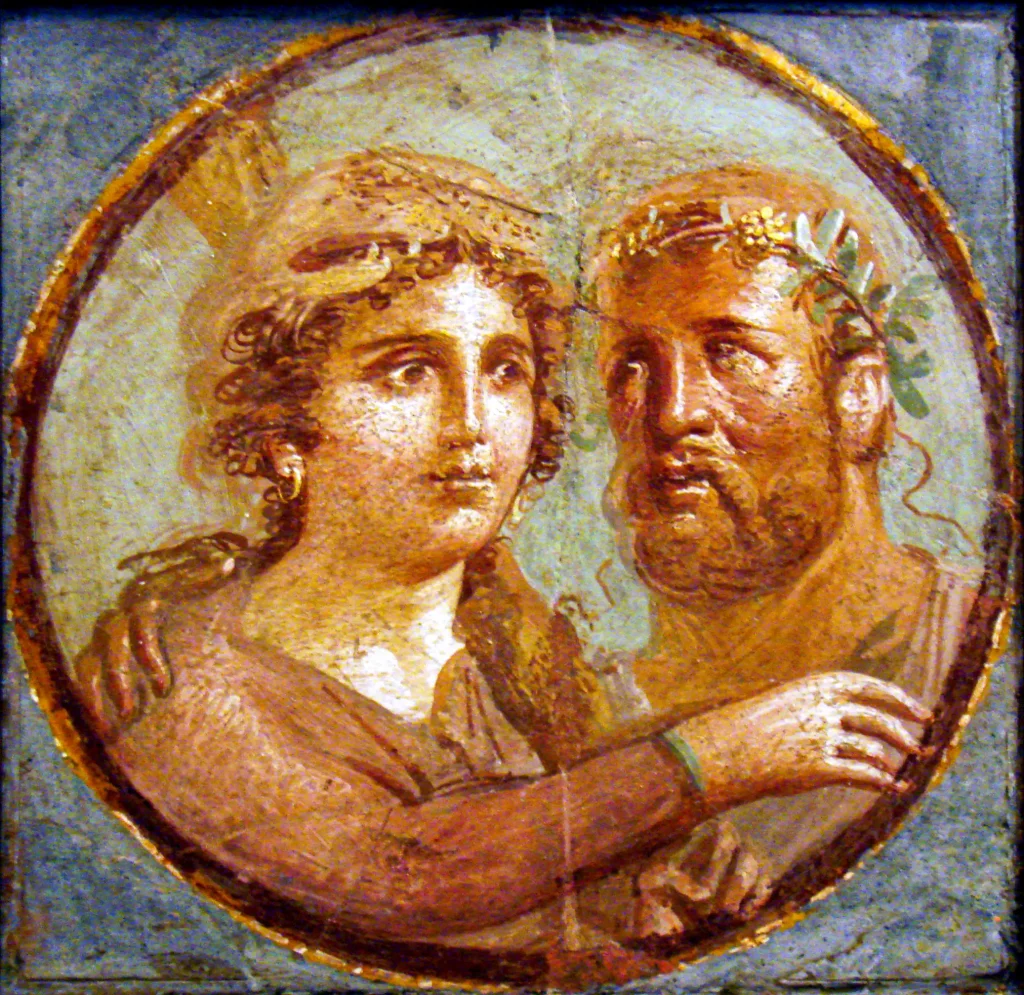
The Romans introduced innovative techniques across various art forms; for instance, their use of frescoes brought vivid colors to life on villa walls, capturing mythological scenes with expressive realism—a tradition that would endure beyond antiquity’s horizon.
Whether commemorating great victories with triumphal arches or celebrating domestic tranquility with wall paintings from Boscotrecase or Pompeii’s House of the Faun, each piece tells a life story during antiquity.

When and Where Roman Art Thrived
Roman art thrived during two significant periods in Roman history: Republican Rome and Imperial Rome. The Republic saw the rise of influential figures such as Augustus, who commissioned many artworks to celebrate his reign.
During Imperial Rome, the arts flourished under the patronage of emperors and wealthy citizens, leading to a wide array of stunning sculptures, monuments, and architectural marvels.
Republican Rome
Republican Rome was a time of rich cultural activity and art. From 509 to 27 B.C., the aristocracy ran the show in Rome. Artists and poets were busy making things that showed their empire’s greatness.
They made statues, painted walls, and crafted beautiful jewelry.
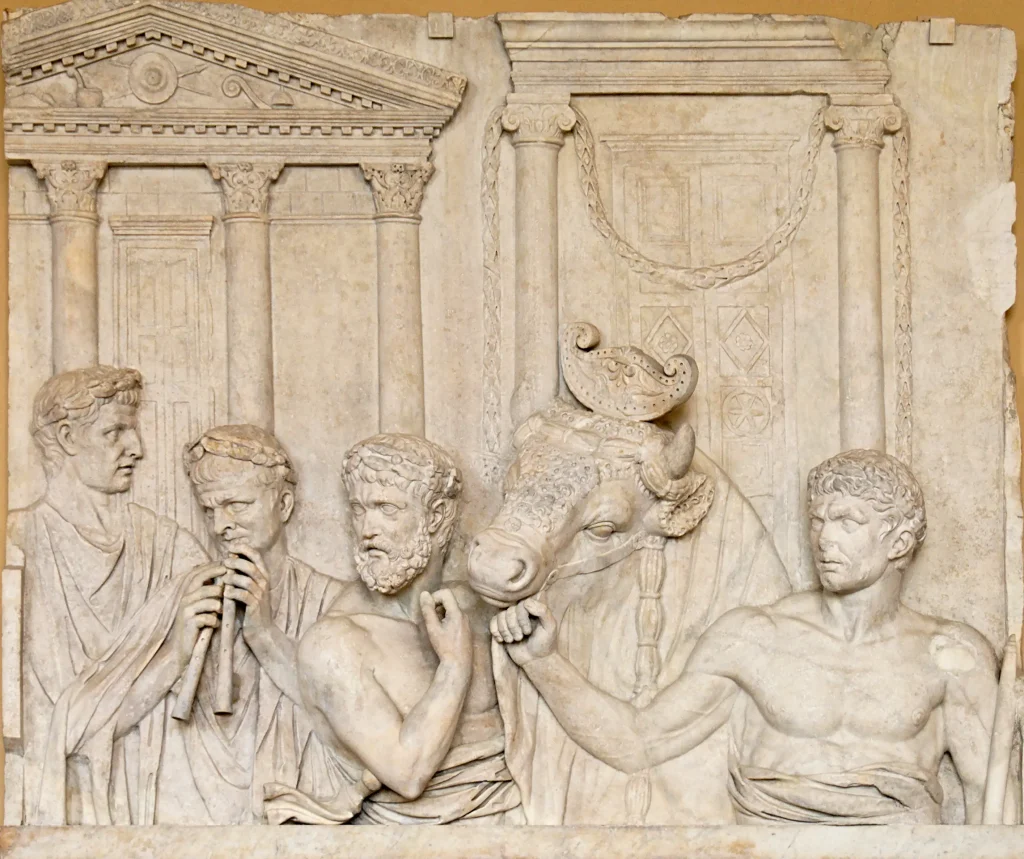
People at this time cared a lot about their history and achievements. They told stories through art on coins, armor, and large stone carvings called reliefs. Temples were built to honor the gods with impressive columns and designs.
Busts of famous people were sculpted to immortalize them. This period set the stage for what was to come—unique artworks that are still admired today!
Imperial Rome
Imperial Rome marked a golden age for Roman art. Starting in 27 B.C., the empire became the heart where artists created lasting works. Marble was key in their craft. They used many kinds from all over to make grand buildings like temples and arches.
This era gave us great treasures like the Colosseum—a sign of Rome’s rich artistic past.
Artists during Imperial Rome were busy. They made statues, paintings, and mosaics that told stories of gods, heroes, and everyday people. Their work still touches our world today—in our laws, languages, and even how we build things.
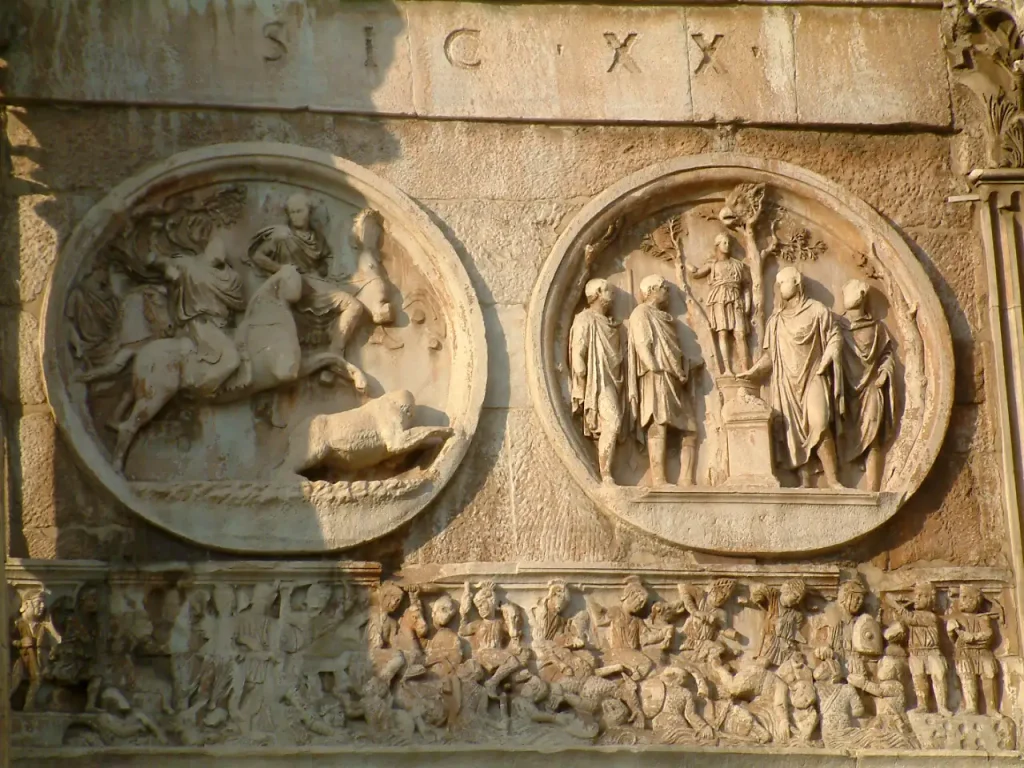
They showed power through images of Emperor Augustus and other leaders. Places like the Ara Pacis celebrated Roman success with detailed carvings. Even simple objects like jewelry or pottery were made with care and precision.
The Creators of Roman Art
Roman art was created by skilled artisans who produced various art forms, including stone and bronze sculptures, ceramics, glass, jewelry, wall paintings, and architectural elements.
Many different people created artworks during the Roman era. Famous artists came from all parts of the Empire and brought their skills to Rome. They worked with marble, bronze, and paint to make beautiful things that showed stories of gods and important events.
Skilled Greek artists were very popular in Rome, and they helped shape Roman style by sharing their ideas.
Craftsmen and artisans from places like Egypt also influenced Roman art. Their work included detailed carvings and colorful paintings that still inspire us today. Famous sculptors and unknown artists left their mark on the world with statues, mosaics, and frescoes that can now be found in museums worldwide.
Next is a look at the key forms of Roman art and what these talented creators produced.
Key Roman Art Forms and What They Created
Roman art forms include seal-cutting, jewelry, glassware, mosaics, pottery, frescoes, statues, monumental architecture, epigraphy, and coins. Here’s a detailed look at each of these key art forms and what they created:
1. Seal-cutting: Intricately carved seals used for stamping or embossing to authenticate documents and goods.
2. Jewelry: Elegantly crafted adornments such as necklaces, brooches, and rings made from precious metals and gemstones.
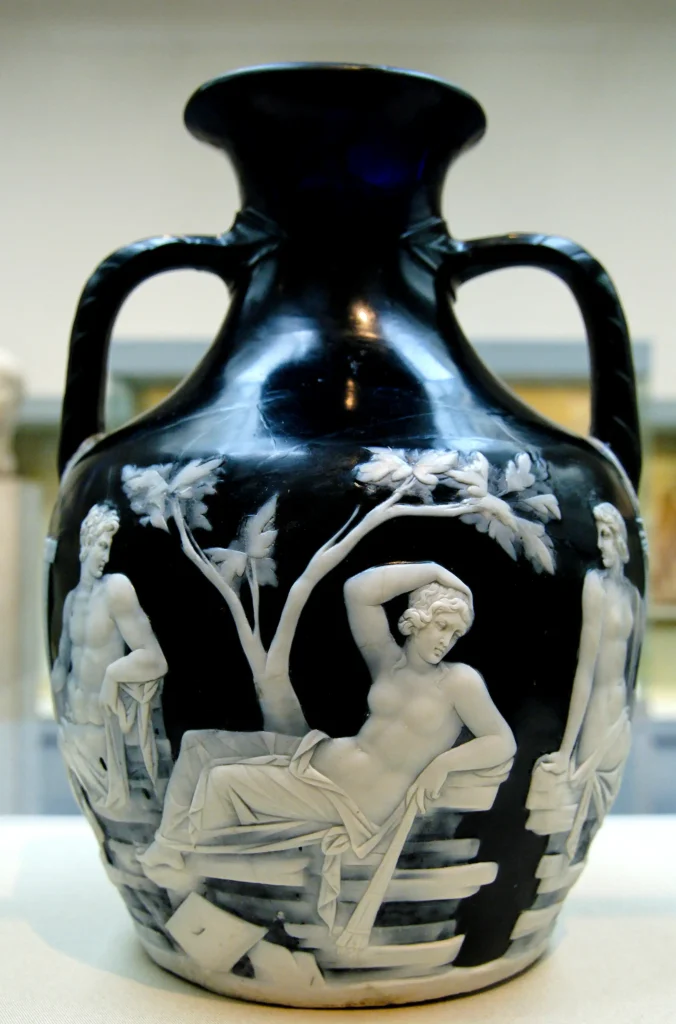
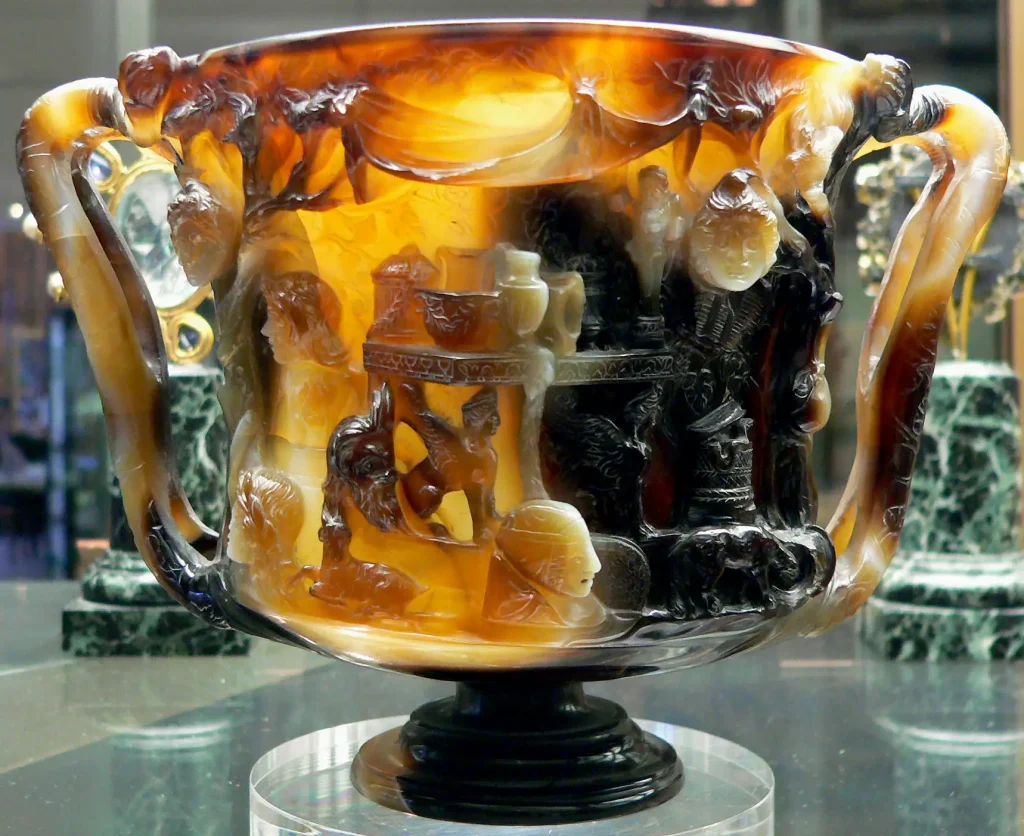
3. Glassware: Delicately designed glass vessels that showcased exquisite craftsmanship, including cups, bowls, and perfume bottles.
4. Mosaics: Stunning artwork composed of small pieces of material fitted together to create intricate patterns or scenes on floors and walls.
5. Pottery: Functional yet beautifully decorated vessels like amphorae, plates, and vases used for daily activities as well as religious rituals.
6. Frescoes: Elaborate wall paintings capturing scenes from mythology, landscapes, and still life compositions in vibrant colors.
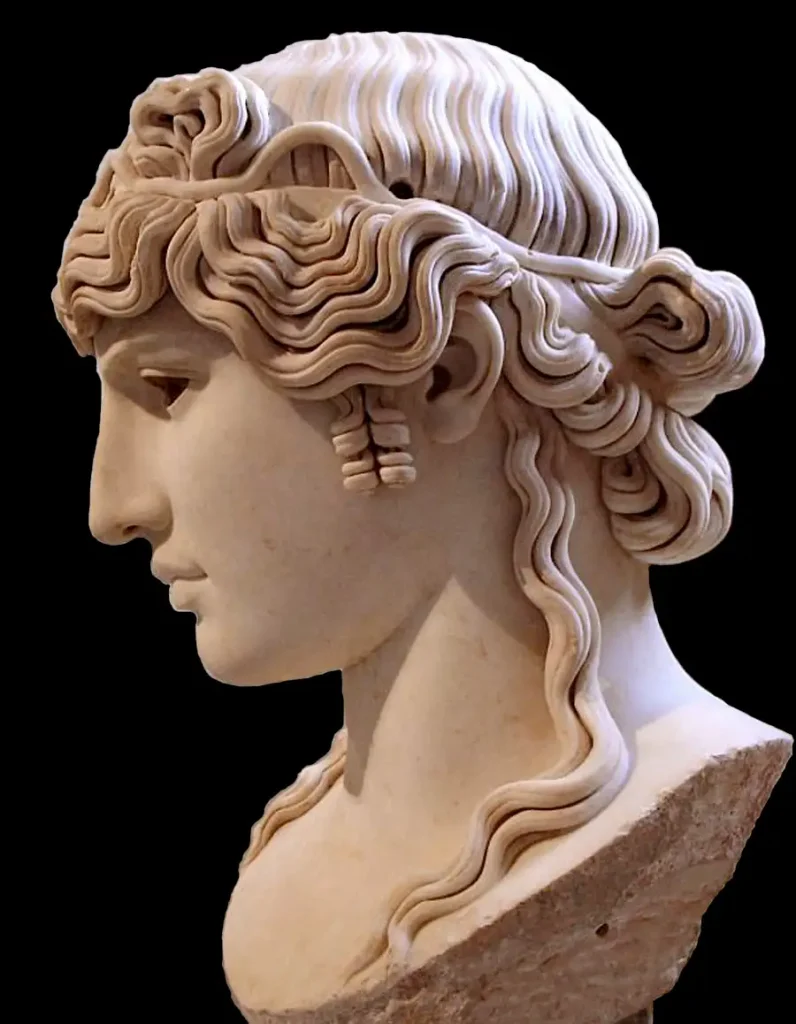
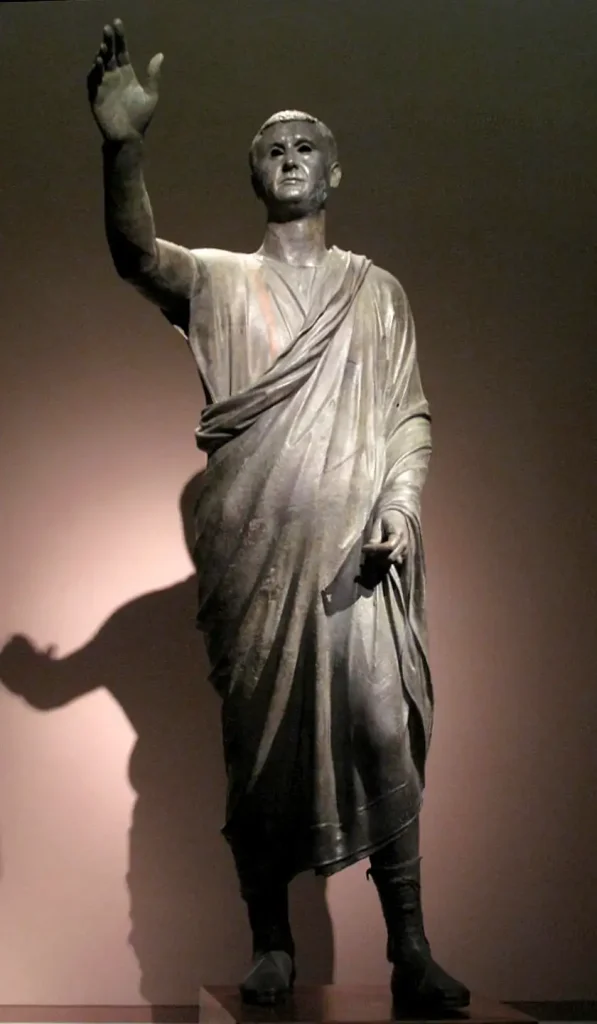
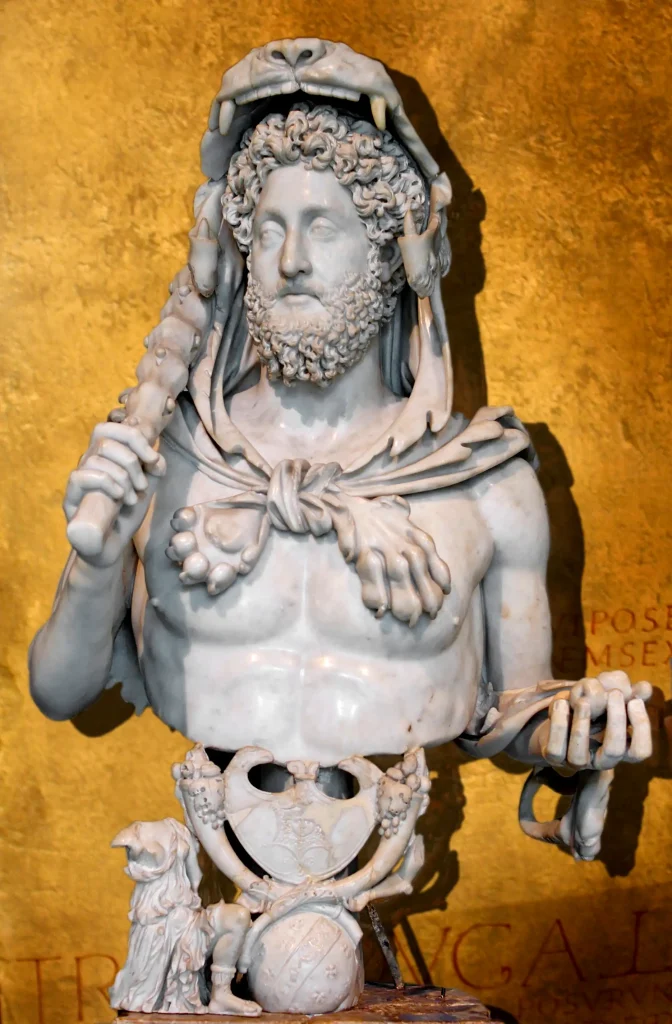
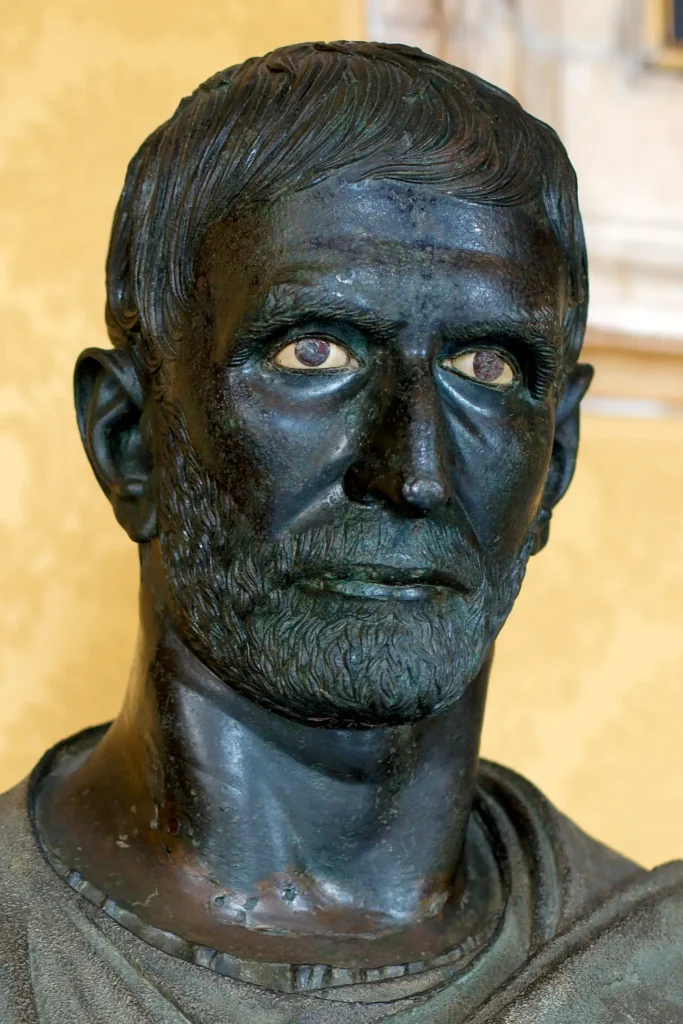
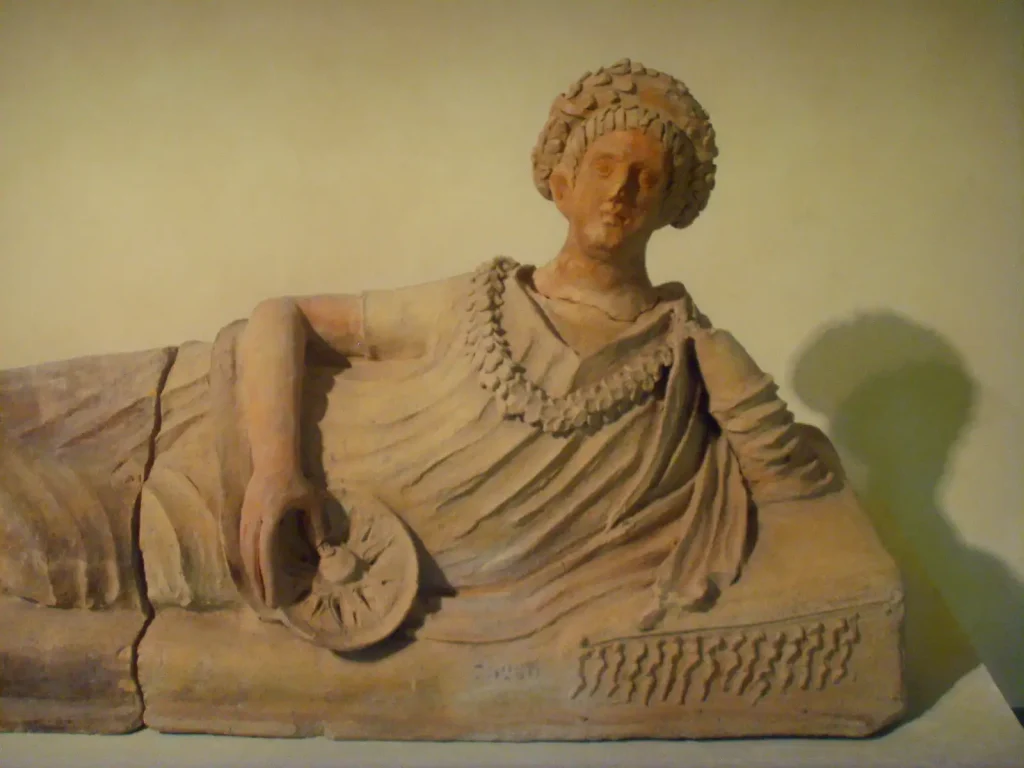
7. Statues: Lifelike sculptures made from marble or bronze depicting gods, mythological figures, emperors, or ordinary citizens.
8. Monumental Architecture: Magnificent structures like temples, bridges, amphitheaters & triumphal arches that reflected Roman engineering prowess.
9. Epigraphy: Inscriptions on buildings or monuments providing historical records or dedications to individuals or deities.
10. Coins: Official currency stamped with images of rulers or significant events serving as a form of propaganda and economic exchange.
Art for All: Rome’s Unique Contribution to Art
Roman art stands out for its accessibility to people from all walks of life. It was not confined to the aristocracy but extended to ordinary citizens and even slaves, making it a unique contribution to art history.
Moreover, Roman artists valued realism and individualism. They depicted real people with imperfections instead of idealized figures. This approach became a defining feature of Roman art, setting it apart from earlier Greek styles.
The Romans also excelled in creating lifelike portraits that conveyed emotion and personality – a skill evident in their exquisite marble sculptures and breathtaking frescoes found in ancient villas and public buildings.
– Roman Artisan Guilds: Skilled artisans across Rome formed guilds that ensured broad access to artistic goods and services. These guilds facilitated the mass production of sculptures, pottery, jewelry, and other decorative items.
– Public Art Spaces: Rome’s public spaces were adorned with sculptures, reliefs, mosaics, and paintings for everyone to admire. Whether in forums, baths, or temples, these artworks became a part of everyday life for Romans.
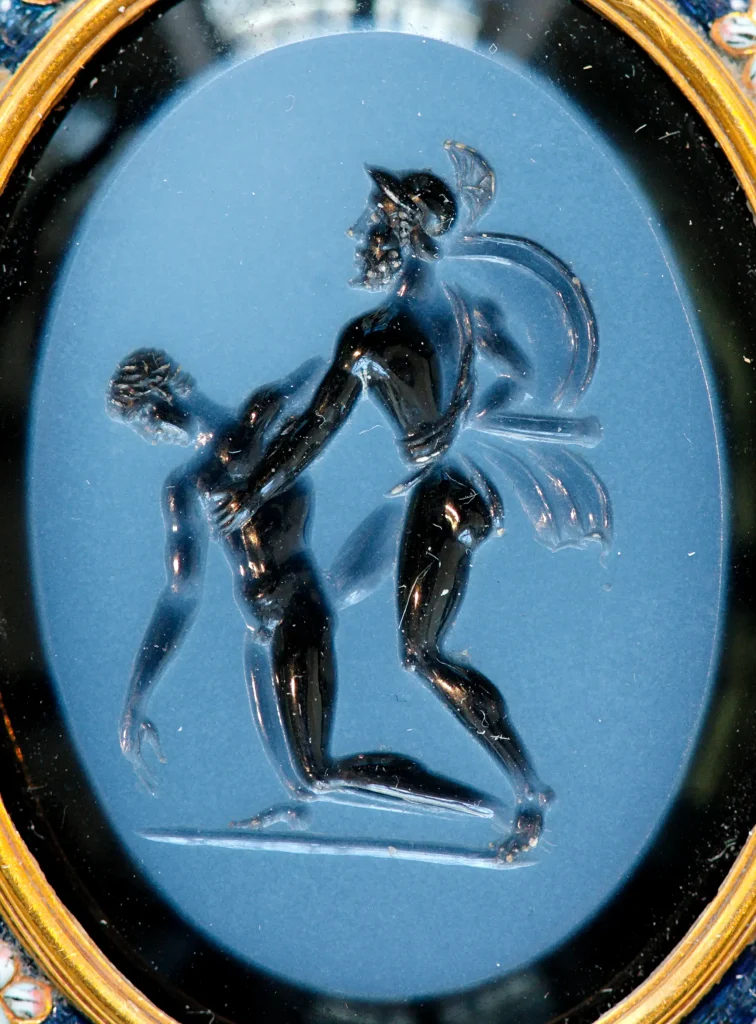
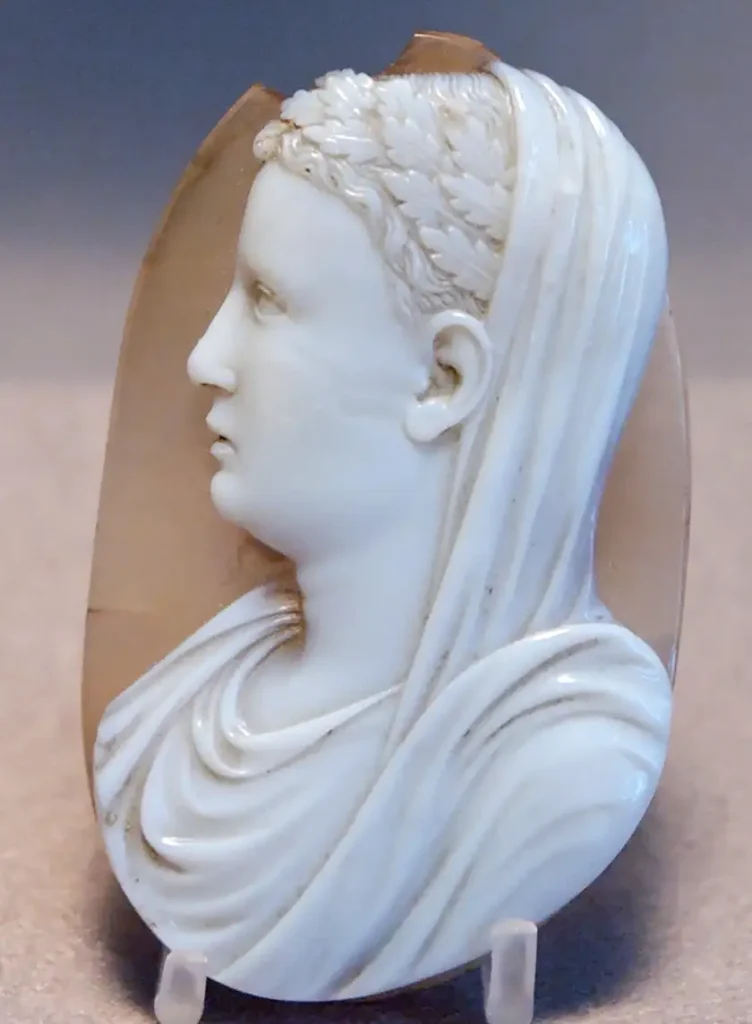
– Portable Art: The portability of Roman art allowed for broader distribution. Miniature sculptures, cameos carved on gems or shells, and small-scale paintings were readily available as personal ornaments or trinkets.
– Household Decorations: Even modest Roman households had access to decorative items such as wall paintings (frescoes), ornate lamps made of bronze or terracotta, and intricate glassware like perfume bottles and drinking vessels.
– Funerary Art: Rich or poor alike could commission funerary portraits or objects, ensuring that every individual had some form of artistic representation even after death.
This inclusivity created an artistic heritage that permeated all aspects of society, from religious rites to household decorations.
Legacy of Roman Art
Roman art has left a lasting legacy, influencing artistic traditions for centuries. The realistic portrayal of subjects in Roman sculpture and the vibrant colors used in wall paintings have continued to inspire artists throughout history.
The influence of Roman art can be seen not only in subsequent Western artistic traditions but also in Eastern art forms due to Rome’s far-reaching empire. Many contemporary artists still draw inspiration from Roman techniques and aesthetics, reaffirming the timeless relevance of this ancient artistic heritage.
– Roman sculptures continue to inspire contemporary artists, reflecting the skill and craftsmanship of ancient sculptors.
– The use of concrete by Romans revolutionized architectural construction, setting a precedent for future advancements in building materials.
– Roman frescoes and mosaics display an intricate combination of color and design, shaping artistic techniques for centuries.
– The grandeur of Roman monuments like the Colosseum and the Pantheon is a testament to the empire’s enduring impact on architectural engineering.
– The development of realistic portraiture in Roman art provided a foundation for portraiture throughout history, capturing individual likenesses with notable precision.
Roman Art in Various Provinces (1-500 A.D)
The art in different Roman provinces from 1-500 A.D. showcased unique styles influenced by the local culture and traditions, offering a diverse perspective of the empire’s artistic legacy.
Roman art varied widely across the different provinces due to each region’s diverse customs and cultures. The influence of local practices and traditions led to a unique blend of artistic styles, resulting in remarkable differences in various parts of the vast Roman Empire.
Various provinces of the Roman Empire, from Britain to Egypt, developed unique artistic styles influenced by their local cultures and traditions, making for a fascinating exploration of Roman art beyond the traditional centers.
The Roman Empire’s diverse regions led to various artistic styles based on their customs and responses to Roman influence. Here are the key influences in various locations:
- North African provinces, like Leptis Magna, embraced Roman-style public spaces and artistic markers, mirroring Italian prosperity.
- Disparate regions followed different customs, resulting in artistic variety, yet Roman practices imposed across the empire also led to diverse artistic responses.
- The emperor’s portrait typically conformed to an official type devised in Rome; however, honorific images often reflected local traditions within each region.
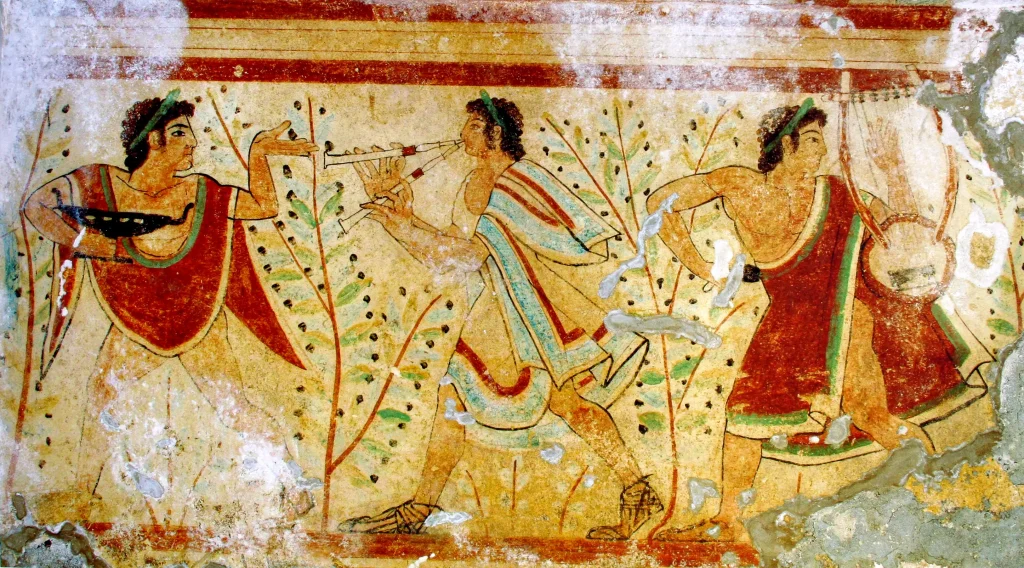
The Impact of Roman Art on the Etruscan Civilization
The Etruscans profoundly influenced ancient Roman culture. The Romans inherited many Etruscan traditions, including their art. The Etruscans flourished in central Italy between 900 and 500 B.C. and were known for their remarkable artistic traditions.
This cultural exchange significantly impacted the development of Roman art, creating a strong link between the Etruscan civilization and Roman artistic expression. This also resulted in the transformation of Etruscan art, incorporating Roman elements that reshaped their artistic expressions.
The Influence of Roman Art on the Byzantine Empire
Roman art significantly influenced the Byzantine Empire, as seen in the luxury of artifacts from the Late, Ptolemaic, and Roman periods. The impact of Roman art extended beyond the empire’s borders, influencing various civilizations such as the Near East, Sumerian, Akkadian, Canaanite, and Babylonian cultures.
The architectural styles and artistic techniques employed by the Romans served as a foundational framework for later Byzantine creations. The incorporation of classical elements into Byzantine art, coupled with an infusion of Christian themes, resulted in a unique amalgamation that defined the visual culture of the Byzantine Empire.
This interplay between classical Roman influences and emerging Christian iconography ultimately produced a distinctive artistic identity that resonated throughout the centuries.
The impact was not solely within visual arts but extended to encompass broader intellectual and cultural facets. The legacy left by ancient Rome profoundly influenced Constantinople’s societal fabric, influencing everything from literature to philosophy.
Through this lens, one can appreciate how Roman art shaped not only physical structures but also the very essence of Byzantine society.
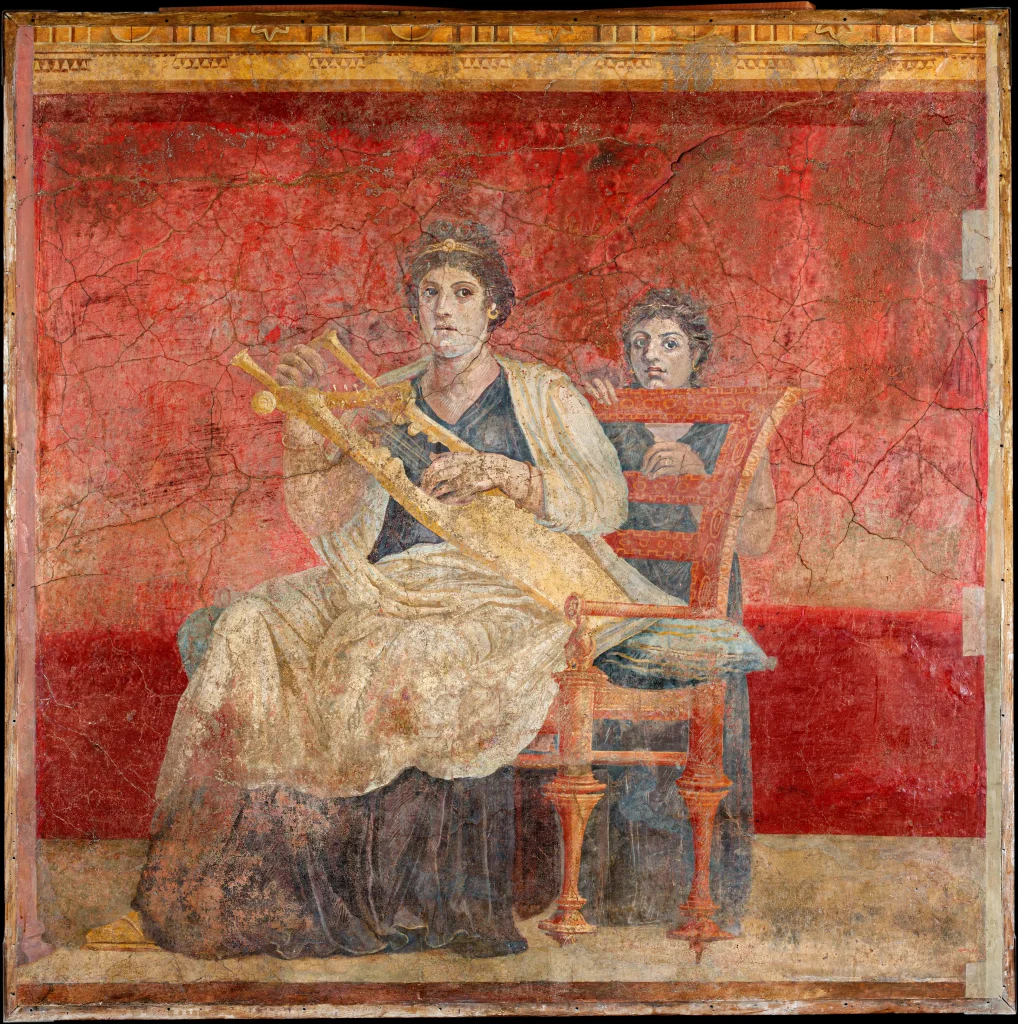
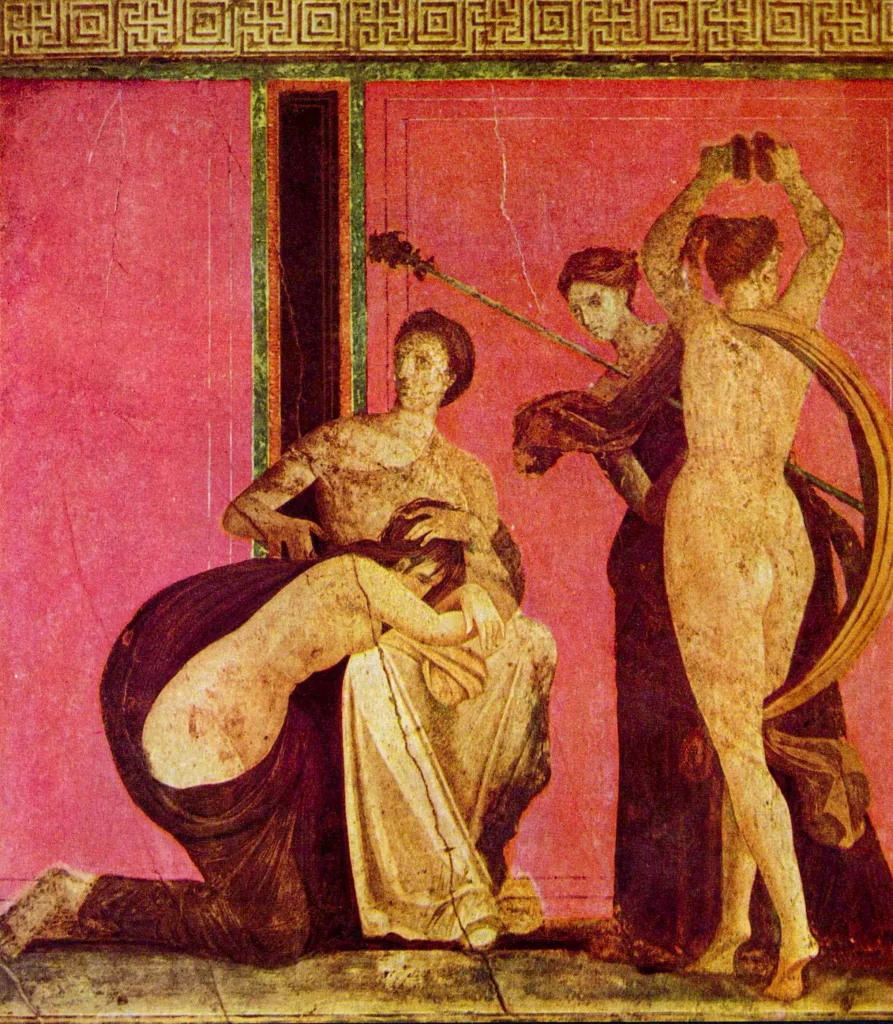
Roman Painting: A Key Art Form
Roman painting was a crucial part of the empire’s artistic heritage. It adorned the walls of homes, villas, and public buildings with vibrant scenes and intricate designs. The themes ranged from realistic portraits to mythological stories, capturing the essence of Roman life.
Frescoes and murals significantly contributed to this art form, showcasing meticulous details and breathtaking colors that added depth and character to interior spaces. These paintings reflected Roman society, its values, beliefs, and aesthetics – providing an invaluable glimpse into their everyday lives.
The artists skillfully utilized different styles, such as the first style, characterized by imitation masonry; the second style featured illusionistic architecture; the third style focused on delicate ornamentation; and the fourth style combined various elements to create elaborate compositions.
Additionally, Roman wall paintings found in Pompeii and Herculaneum offer a wealth of insights into ancient Roman culture through their detailed depictions of landscapes, still lives, and scenes from mythology and history – bringing forth a dynamic visual storytelling tradition that continues to captivate audiences even today.
Roman Art and Architecture: An Unbreakable Bond
Moving from the significance of Roman painting to its unbreakable bond with architecture, it’s evident that these two art forms intertwined seamlessly in ancient Rome. The Romans were not only adept at creating stunning works of art but also possessed remarkable architectural skills.
Their concrete and domed temples, ornate arches, regal amphitheaters, and ingenious aqueducts stand as testimony to their extraordinary architectural prowess. Moreover, the renowned Colosseum serves as an exceptional representation of the opulent artistic heritage of the Roman civilization.
The imprint of Roman art and architecture extends beyond just their era. Early Christian art and architecture demonstrate a profound influence from Roman forms. Notably, early Christian churches were often based on Roman assembly halls, directly reflecting this influence.
This connection underscores the deeply rooted bond between Roman art and architecture, transcending time periods and cultural shifts.
Chronology of Roman Art
Roman art can be divided into distinct periods, each characterized by unique artistic styles, techniques, and influences. Understanding the chronology of Roman art helps in appreciating its evolution and the impact of historical events on artistic expression. Below are the key phases of Roman art:
- Etruscan Influence (8th – 6th century B.C.): Etruscan culture heavily influenced early Roman art, which is evident in terracotta sculpture and bronze works.
- Republican Rome (509 – 27 B.C.): During this period, portraiture gained prominence, and public architecture, such as temples and basilicas, reflected Greek influence.
- Imperial Rome (27 B.C. – 476 A.D.): The era of Emperor Augustus saw a flourishing of marble sculpture and grand architectural projects like amphitheaters and baths.
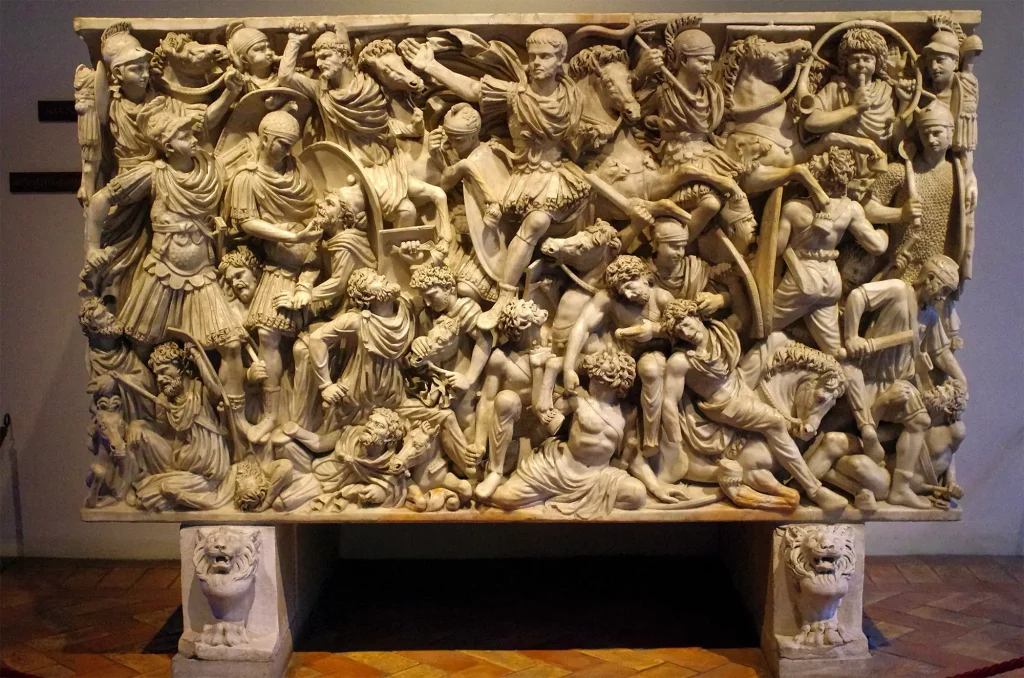
- Severan Art (193 – 235 A.D.): Characterized by elaborate relief sculptures and an emphasis on luxury artworks reflecting wealth and prestige.
- Late Antiquity (3rd – 6th century A.D.): Artistic expression shifted towards Christian themes, with mosaic art adorning churches and catacombs.
Significant Figures in Roman Art
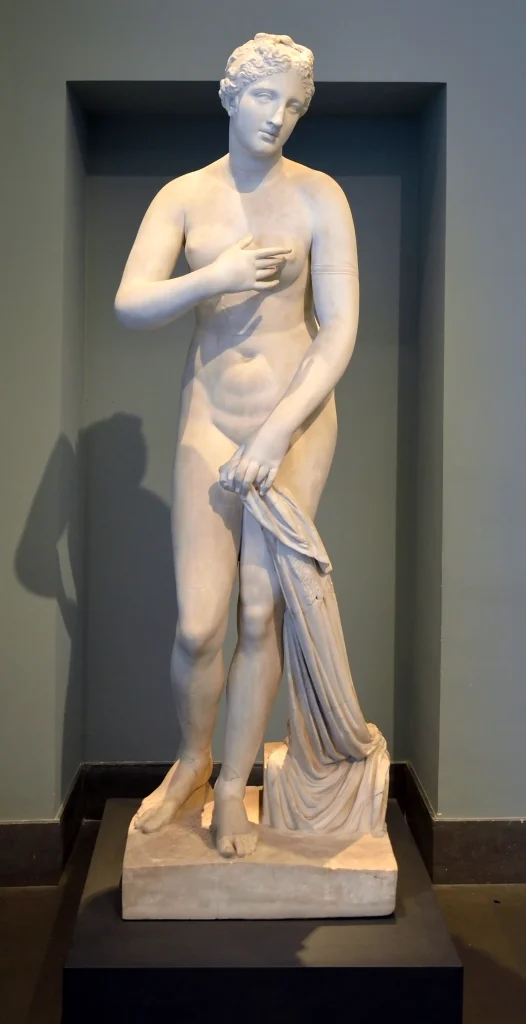
Roman art boasts significant figures who have left an indelible mark on history. One such figure is Praxiteles, a renowned Greek sculptor known for his lifelike portraits, who profoundly influenced Roman marble sculpture.
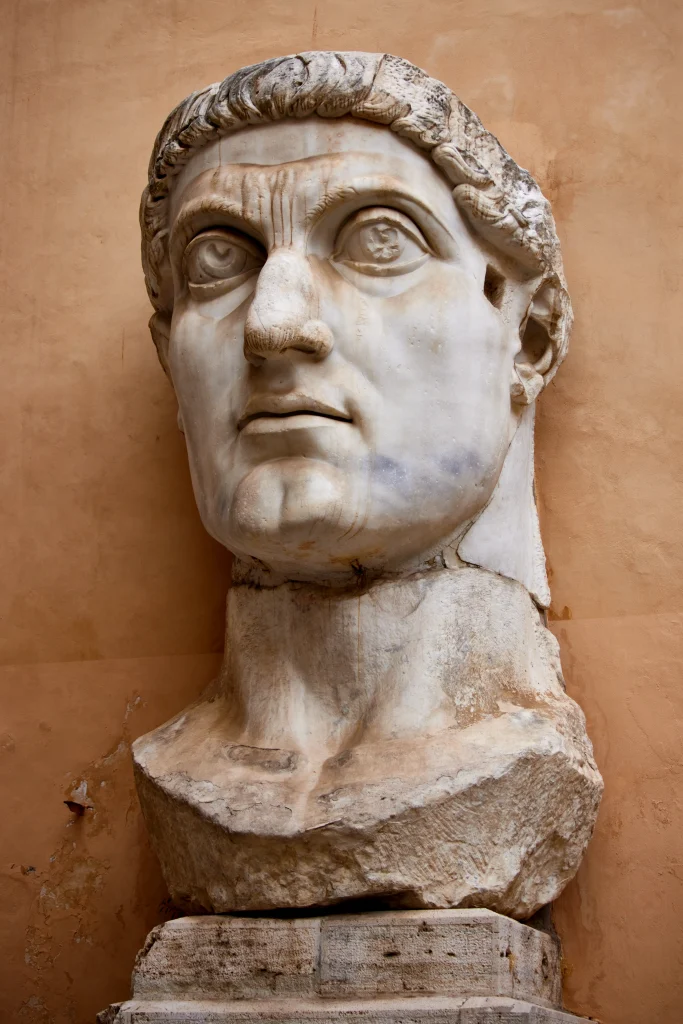
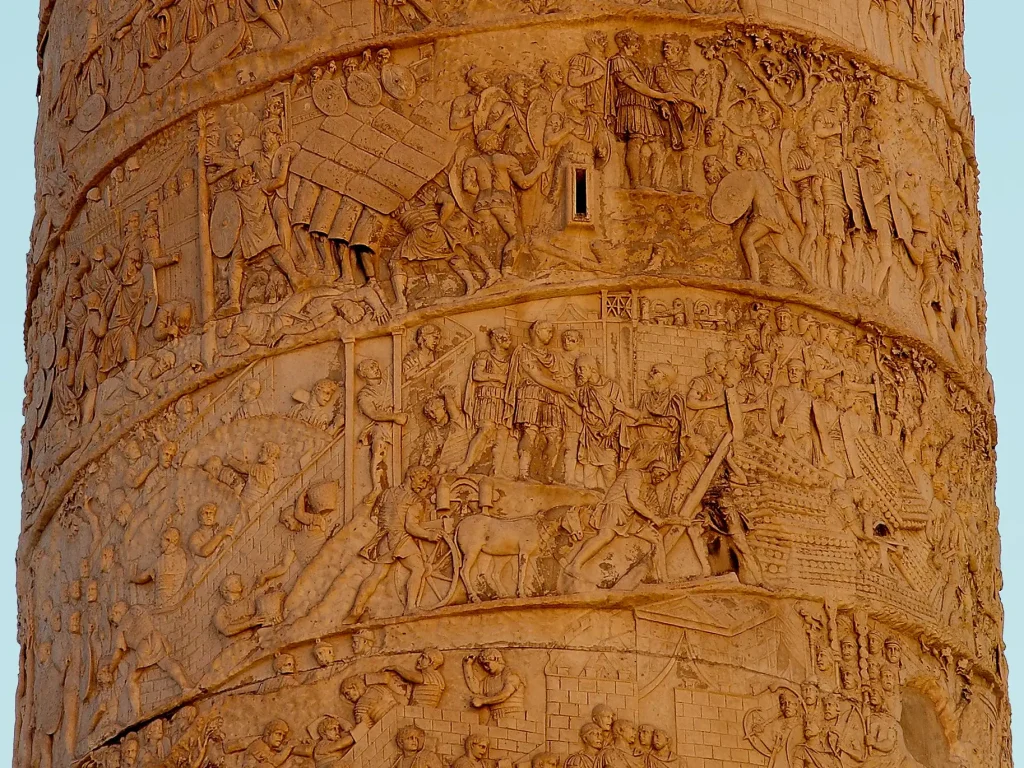
His creation, “Aphrodite of Knidos,” was celebrated for its innovative portrayal of the female form, reshaping beauty standards in ancient art. Another influential figure is Constantine I, whose reign witnessed a flourishing period for Roman art and architecture.
Notably, his triumphal arches stand as enduring testaments to his patronage of artistic endeavors.
Artistry flourished under the rule of Augustus, with the impressive Ara Pacis serving as one of his enduring legacies. This altar embodies not only exceptional skill but also reflects Augustus’s vision for promoting peace and prosperity through visual representation.
Additionally, Severan art emerged during the reigns of Septimius Severus and his dynasty, highlighting a distinctive blend of Eastern and Roman styles that enriched the artistic landscape.
As one gains a deeper understanding of these significant figures’ contributions to Roman artistry, it becomes evident how their creative brilliance continues to captivate audiences worldwide.

Popular Online Resources for Further Exploration of Roman Art
Exploring the world of Roman art doesn’t have to be limited to physical museums and galleries. The digital sphere offers many resources for diving deeper into this captivating artistic heritage. Here are some popular online resources to aid in your exploration:
- Roman Art: A Resource for Educators: A comprehensive 218-page publication offering an introduction to ancient Roman art informed by recent research.
- Perseus Digital Library: As a treasure trove of ancient texts, images, and archaeological data, this resource offers a unique perspective on Roman art through its extensive collection of digitized artifacts and scholarly resources.
- Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History: This comprehensive online resource presents a wealth of information on various aspects of Roman art, from sculpture and architecture to painting and decorative arts.
Conclusion
Ancient Roman art is a rich tapestry of creativity and innovation, blending influences from various cultures to produce remarkable masterpieces. By exploring the opulent artistic heritage of the Roman Empire, we can uncover a world filled with vibrant sculptures, intricate mosaics, and expressive paintings that continue to captivate and inspire.
With an array of practical insights into this fascinating realm, readers can gain fresh perspectives on Roman art and its enduring impact on history and culture. Further reading materials and online resources are available to delve deeper into this captivating subject.
Embracing the artistic legacy of the Romans opens doors to understanding our shared human experience across millennia.
FAQs
1. What kinds of art did the Romans create during their empire?
The arts of ancient Rome included stunning statues of Aphrodite—the Greek goddess of love—finely carved gems and captivating pottery vessels. They also painted walls with scenes from mythology and made intricate jewelry such as brooches and necklaces.
2. Did Roman art come only from Rome itself?
No, not at all! The Roman Empire was massive, stretching over many lands. You’d find examples of Roman art in cities like Leptis Magna—an important city under Roman rule—and treasures in homes from Herculaneum to Boscoreale.
3. Did the Romans only create statues of gods and goddesses?
No—they made lots more! From busts of emperors like Septimius Severus to funerary art such as sarcophagi with battle scenes or tender mummy portraits, it wasn’t just divine figures but also things representing daily life or important events.
4. Are there famous works from Rome I can still see today?
Absolutely! You can check out stunning pieces at museums around the world—for example, the Museo Nazionale Romano, Palazzo Altemps, has a fantastic collection or visit spots like Leptis Magna, Herculaneum, or Boscoreale to see beautiful artifacts and architecture preserved for all to enjoy.
5. Why should we care about ancient funerary arts today?
Well, funerary arts give us glimpses into past lives—showing what people valued through statues or even household gods called lararia placed in tombs for protection in the afterlife.



































